语音关键词检测方法综述
参考:《语音关键词检测方法综述 白烨.pptx》
[TOC]
主流方法 Mainstream Approaches
Keyword Spotting”、“Keyword Search”、“Spoken Term Detection”,
语音检索:从大段语音文档中定位到关键词所在位置。语音关键词检测相关的英文术语有“Keyword Spotting”、“Keyword Search”、“Spoken Term Detection”,然而它们实际上有不同的侧重,是两类不同的问题。Keyword Spotting 指的是语音设备控制这一类应用,一般来说它的关键词是固定的,关注的是低内存占用,低计算复杂度,低功耗下的高准确率;Spoken Term Detection或Keyword Search的关键词一般是可变的,需要定位出关键词在音频文档中的位置,困难点在集外词问题。下面我们分别就这两类问题,介绍相关的三种主流方法,然后在介绍几个前沿进展,最后做一个总结。
语音唤醒:Keyword Spotting,用于Voice-controlled devices
- 特点:Keywords are usually fixed、Small-footprint、Efficient computation、Low-power consumption
语音检索:Spoken Term Detection(Keywords Search),用于Searching keywords in audio,在一大段语音音频中找到多个关键词
- 特点:Keywords are changeable、Need to locate the keywords in audio、Out-of-vocabulary
1、补白模型(Filler Models)
补白模型有时也被称为垃圾模型,它将Keyword Spotting问题考虑为一个逐帧的序列标注问题。关键词定为不同的标注,而一个额外的“补白”标注用来匹配所有非关键词。(序列标注:关键词,关键词,关键词,非关键词,非关键词,非关键词,…..这样的序列,多少帧多少标注,找最优路径,词级别的建模 –yl)
基于隐马尔可夫模型的补白模型最早用于Keyword Spotting。它对每一个关键词建立一个隐马尔可夫模型,对非关键词额外建立一个隐马尔可夫模型,观测概率通过混合高斯或神经网络建模。直接针对关键词建模在数据稀疏的问题。目前流行的隐马尔可夫模型则采用子词单元,如音素,进行建模。这种情况下,它与基于HMM混合模型的语音识别中的声学模型就十分类似了,只是解码图是手工设计的文法,而不是基于统计语言模型生成的。亚马逊Alexa语音助手所用的Keyword Spotting系统就是基于这一类方法的。
- The filler models are sometimes known as garbage models or acoustic keyword spotting.
- This model can be seen as a framewise ==sequence labelling== problem.
- Keywords and non-keywords are modeled respectively in this approach.
- Filler models are a set of models which can match ==arbitrary non-keyword== speech utterances.
HMM based filler models
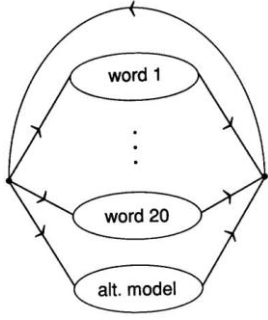
- Each keyword and a filler are modeled using HMM respectively.
- Generative probability of a frame of speech parameters given a state of HMMs is estimated with GMMs or DNNs.
Wilpon J G, Lee C, Rabiner L R, et al. Application of hidden Markov models for recognition of a limited set of words in unconstrained speech[C]. international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 1989: 254-257.
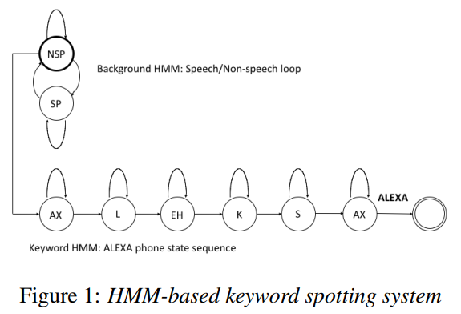
- Each phone is modeled by an HMM model.
- Searching Graph is built with a handcraft phone-level grammar. 手工打造的
Sun M, Snyder D, Gao Y, et al. Compressed Time Delay Neural Network for Small-Footprint Keyword Spotting.[C]. conference of the international speech communication association, 2017: 3607-3611.
DNN based filler models
另一种基于神经网络分类的方法就更加直接了,如下图所示,连续语音流逐段地送入神经网络进行分类。类别为所有的关键词,和一个额外的填充类别(Filler),比如有10个关键词,就有11类。
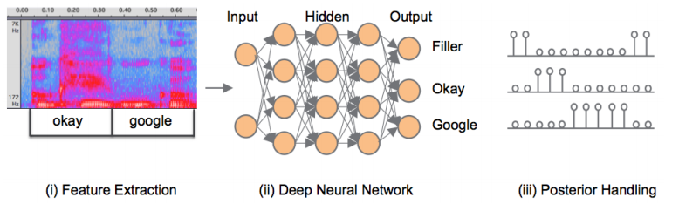
分类完成后,由于输出的概率可能出现“毛刺”,所以进行平滑后处理,之后如果某一个类别概率超过一个阈值,就认为某一个关键词被检测到了。这种方法内存占用小,不需要解码搜索,准确率高。但是由于需要准备大量包含关键词的语料,如果更换了关键词,则需要再另行搜集一批语料,所以也较难实际使用。相比之下,基于隐马尔可夫模型的Keyword Spotting由于是针对子词单元建模,语料用通用的就可以,所以更常用。
(一段语音一段语音地送入DNN,得到这一段语音,比如100帧的100个输出,每个输出有11分类的概率,平滑一下,看看关键词分类的概率是否高过阈值,判断关键词是否被检测到–yl)
- DNN is used as a framewisely classifier.
- Then the posteriors are smoothed with a window.
- The system is used in mobile devices.
Chen G, Parada C, Heigold G, et al. Small-footprint keyword spotting using deep neural networks[C]. international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 2014: 4087-4091.
2、基于样例的Keyword Spotting (Query-by-Example)
基于样例的Keyword Spotting,则将问题考虑为匹配问题。考虑关键词的音频样例,和几个测试音频,分别计算它们的相似度,测试音频中和关键词相似度超过某个阈值的,就认为它是检测出来的关键词。这种方式在使用的过程中,用户可以录制自己的音频并定义为关键词,使用起来就更个性化。
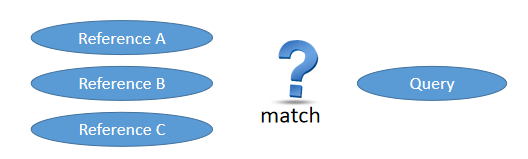
- Query-by-example is a task to detect some keywords in a speech signal, where the keywords are saved as ==patterns==.
- Query-by-example methods allow users define their own keywords. It is more ==personalized== for them to control their own devices.
Query-by-example methods
基于样例的关键词检测可以分为两类,一种基于动态时间弯折(Dynamic Time Warping,DTW)算法,它使用DTW算法计算两个音频特征序列之间的相似度;另一种是基于嵌入学习的,它将两个音频分别编码为向量,然后直接计算两个向量之间的距离。基于DTW的方法从上世纪70年代就开始开始应用,但是它在匹配两个序列的时候计算复杂度比较高,目前主要用于无监督的情形;基于嵌入学习的方法,匹配的时候更为简单,在深度学习火热以后就流行起来。
- DTW Based Methods
- Extended from isolated word speech recognition.和孤立词识别方法一样,计算dtw距离,判断一段语音是不是关键词
- The main difference is that the query is a word and the reference may be a longer sentence.和孤立词识别不同的是,query是词,reference是长句子
- Embedding Learning Based Method
- Represent speech sequence of arbitrary length as a fixed-dimensional vector are used in KWS.把任意长语音序列embed到固定维度向量
DTW Based Methods
- Compute similarity between two sequences of vectors. 用动态规划 计算两个向量的相似度
- Two stages:
- Convert the queries and target speech into same representations using acoustic models.通过声学模型得到query和target speech的输出
- Compute confidence of appearance of the keywords to decide whether the keywords appear in speech stream. 计算keyword置信度
Itakura F. Minimum prediction residual principle applied to speech recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1975, 23(1): 154-158.
Sakoe H, Chiba S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken word recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1978, 26(1): 159-165.
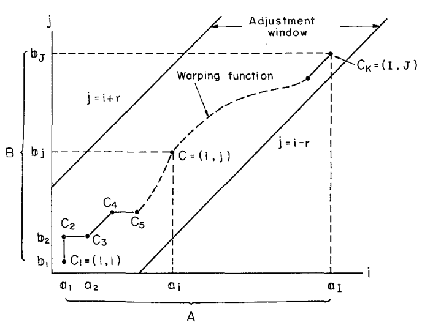
Formally Given two sequences $X=x_1,…,x_N$、$Y=y_1,…,y_M$
Consider 累计距离 $c(k)=(i(k),j(k))$
The matching pattern is a sequence of points $F=c(1),c(2),…,c(k),..,c(K)$
The time-normalized distance is defined as:
$$
D(X,Y)=\min_F{\frac{\sum\limits^K_{k=1}d(c(k))w(k)}{\sum\limits_{k=1}^Kw(k)}}
$$
与长度有关,因此要归一化。
约束条件 Five constraints:
Monotonicity $i(k-1)\leq{i(k)}$ and $j(k-1)\leq{j(k)}$
Continuity $i(k)-i(k-1)\leq1$ and $j(k)-j(k-1)\leq1$
Boundary $i(1)=1$, $j(1)=1$ and $i(K)=N$, $j(K)=M$
Adjustment window $|i(k)-j(k)|\leq{R}$
Slope constraint
Several variants of DTW for KWS
原先用于孤立词的DTW,用于KWS时,要做一些变化,因为一段语音里有很多内容,不确定匹配的有没有命令词。可以做分段DTW,也就是每隔一段语音就做一次DTW,看看和命令词的相似度;也可以做不分段的DTW,通过距离找到和模板第一个特征距离最小的测试语音的位置,然后才做DTW。
Segmental DTW
Segmented DTW
Non-segmental DTW
Subsequence DTW
Segmental local normalized DTW
Mantena G V, Achanta S, Prahallad K, et al. Query-by-example spoken term detection using frequency domain linear prediction and non-segmental dynamic time warping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014, 22(5): 946-955.
Zhang Y, Glass J R. Unsupervised spoken keyword spotting via segmental DTW on Gaussian posteriorgrams[C]. ieee automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop, 2009: 398-403.
Segmental DTW:
每隔一段语音就做一次DTW,看看和命令词的相似度;
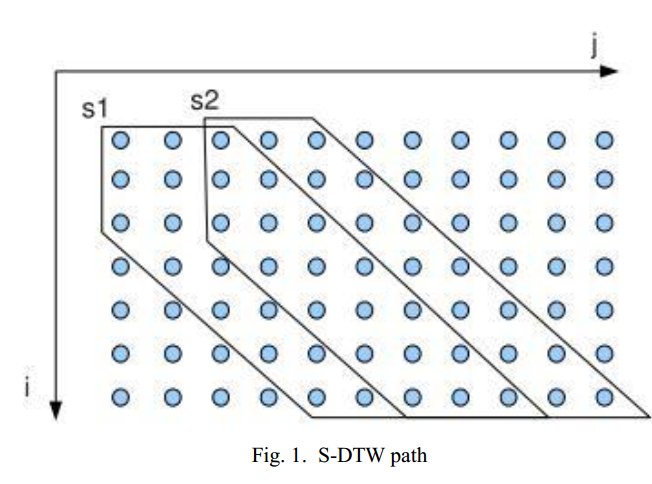
Segmental local normalized DTW
Time complexity of SLN-DTW is O(mnd)
Feature representations and distance computation 特征表示和距离计算
- Main feature representations
- Acoustic parameters (MFCC, FBANK)
- Posteriogram (GMM, DNN)
- Bottleneck feature (DNN, Autoencoder)
- Distance computation
- Compute similarity at each DTW step
- Euclid distance
- $-log(x\cdot{y})$ (对数内积)
- $1-\frac{x\cdot{y}}{|x||y|}$ (1 - cosθ)
Some drawbacks of DTW
- Comparing two sequences using DTW based methods costs polynomial time.计算相似度耗时高(多项式的时间)
- DTW is often oversensitive to longer phonetic segments. (长的音素段会过敏感)
Embedding Learning Based Method
- General ideas of non-DTW methods are based on to construct a ==fixed-dimensional vector== to represent a speech segment of arbitrary length.
- In this case, common distances such as Euclid or cosine can be used to measure similarity between two sequences.
Embedding learning using LSTM
Audio is preprocessed by a voice activity detection system.
For speech regions, 40-dimensional mel-filterbank features are generated.
15k output targets represent whole word units
A fixed-length representation $f$ is created by choosing the last $k$ state vectors.
如图所示就是一个基于嵌入学习的关键词检测系统。它由一个LSTM网络构成。训练时,将LSTM视为一个词级别的分类器;测试时,将测试音频和关键词音频输入进LSTM,将最后k个状态拼接起来,计算余弦距离,如果超过某个阈值,就认为是检测到了关键词。
Chen G, Parada C, Sainath T N, et al. Query-by-example keyword spotting using long short-term memory networks[C]. international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 2015: 5236-5240.
Siamese networks based on CNN 孪生网络
雷博说,孪生网络是人脸识别中提出的,可以比较两张人脸的相似度
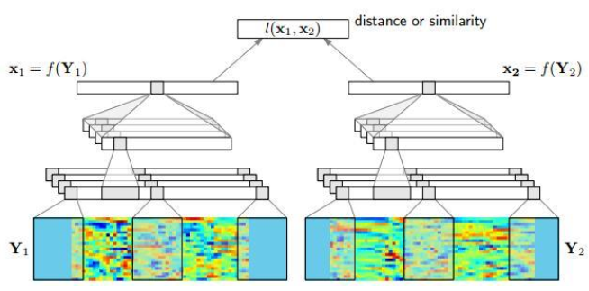
- Weakly supervised: the transcripts of training data and testing data are unknown.
Kamper H, Wang W, Livescu K, et al. Deep convolutional acoustic word embeddings using word-pair side information[J]. international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 2016: 4950-4954.
3、基于大词汇量连续语音识别系统的关键词检测(LVCSR Based Methods)
基于大词汇量连续语音识别系统的关键词检测主要是用于音频文档检索任务。首先使用语音识别系统将语音转化为某种形式的文本,然后建立索引,供用户索引。

与一般文本索引不同的是,语音关键词检索中的索引需要包含每一个词的时间位置信息,方便用户定位检索到词的位置。另外一点就是,语音识别结果可能包含一些错误,导致关键词不能找到,所以希望索引将语音识别出的次优候选结果也包含进来,提高检索的召回率。针对这两点的主要方法是,将语音识别出的词格(Lattice)建立为索引。词格是一种保存语音识别候选结果的紧凑形式,还可以包含时间位置信息。
- The recognition results of LVCSR may contain errors, which will hurt the keyword spotting effect.
- How to index raw result of ASR?
- Location of each word
- Lattice
Lattice
- A lattice is a compact representation of ASR results.
Timed Factor Transducer
因子自动机?
A TFT is a WFST mapping each factor x:
- the set of automata in which x appears;
- start-end times of the intervals where appears in each automaton;
- the posterior probabilities of actually occurring in each automaton.
Indexing
- Convert lattices to TFTs
- Union
- Optimize
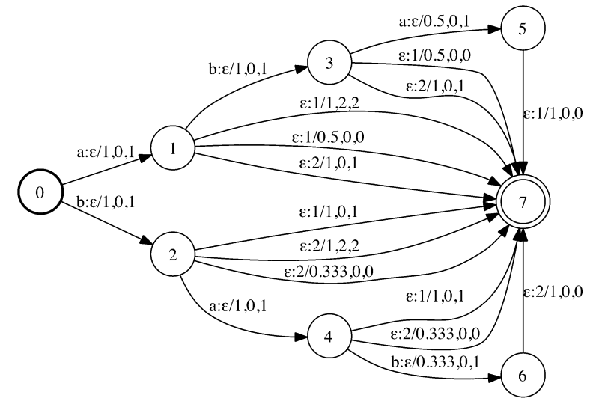
当前比较流行关键词检索的索引是时间因子转换器(Timed Factor Transducer,TFT),在著名的语音识别工具包Kaldi中已经被实现。它可以在线性复杂度下检索到关键词。具体的TFT的构建需要大量背景知识,这里就不展开介绍,详细请见参考文献。
Can D, Saraclar M. Lattice Indexing for Spoken Term Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2011, 19(8): 2338-2347.
TFT for Lattice Indexing
- Searching
- Convert query to a linear acceptor X
- Compose X and T: R
- Each successful path in R is a single arc, the label is the automaton id, and a (LogP, start-time, end-time) triplet.
OOV problem
由于语音识别的结果都是在词表内的词,这样如果待查的关键词是集外词,就不可能被查找到了。然而,用户喜欢查找的,往往是人名、地名、组织机构名这样的命名实体,这些词往往都是集外词。解决这一问题的一个方法是代理词:即用一个发音相近的集内词作为待查集外词的“代理”,检索的时候查找“代理”,如果找到了代理,就认为待查的集外词找到了。
(前面从音频特征或者embedding到向量,都是从音频出发,不会有asr识别过程,因此没有oov问题–yl)
- The out-of-vocabulary problem is more important in KWS than in ASR.
- Users often would like to search names or new words which are out-of-vocabulary.
- A basic approach to tackle OOV problem is using sub-word units such as phones or syllables as results of the LVCSR system.子词
Proxy word: a unified process method 代词
- Proxy words are IV keywords which are acoustically similar as OOV keywords.
- In spotting stage, proxy words are searched in the index instead of original out-of-vocabulary query.
Chen G, Yilmaz O, Trmal J, et al. Using proxies for OOV keywords in the keyword search task[C]. ieee automatic speech recognition and understanding workshop, 2013: 416-421.
Proxy words generation
- Proxy words are generated based on WFST $K’ = Project(ShortestPath(K\circ{L_{2}}\circ{E}\circ({L^{*}_1})^{-1}))$
- where K is a FSA for an OOV keyword
- L2 a FSA for the pronunciation of the OOV keyword
- E is an edit-distance transducer
- L1 denote the pronunciation lexicon of the LVCSR
- K’ is a FSA corresponding to proxy words
Phone confusion matrix estimation
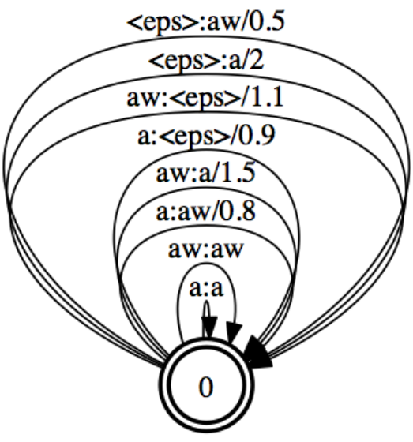
边上权重:相似度
The phone confusion matrix is generated using maximum likelihood estimation.
The pronunciations of the words are obtained using G2P software.
前沿进展 Some Advances
Model Compression
TDNN
在HMM补白模型方面,亚马逊在2017年Interspeech发表了一篇声学模型压缩的文章。具体上,采用时延神经网络(Time Delay Neural Networks,TDNNs)以及降采样结构来减小模型参数,进一步地,还使用了SVD分解,将大的仿射变换矩阵分解为两个小的矩阵相乘的结构,大大减小了参数量。
TDNN优点:可以跳帧
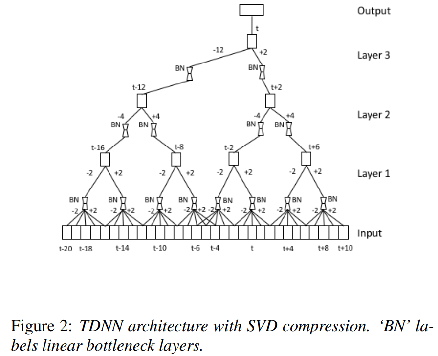
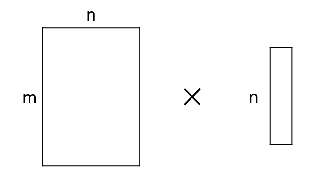
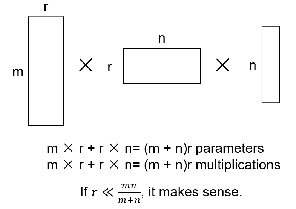
SVD分解
$mn$的矩阵运算,变为$mr+r*n$,当$r\ll\frac{mn}{m+n}$时,能节省很多运算量(虽然两个矩阵的秩变小了)
Sun M, Snyder D, Gao Y, et al. Compressed Time Delay Neural Network for Small-Footprint Keyword Spotting.[C]. conference of the international speech communication association, 2017: 3607-3611.
Compute similarities between heterogeneous patterns
基于神经网络来计算异质数据之间相似度的关键词检测。具体上,对于音频用一个循环神经网络来提取高层特征,而对于文本关键词,则采用卷积神经网络来提取高层特征,然后利用多层感知机来判断这两个高层特征是否匹配。由于语音和文本是两个模态的数据,以往的方法很难去计算它们的相似度,而深度神经网络的强大特征映射能力则给我们带来了直接计算两个模态数据相似度的可能。
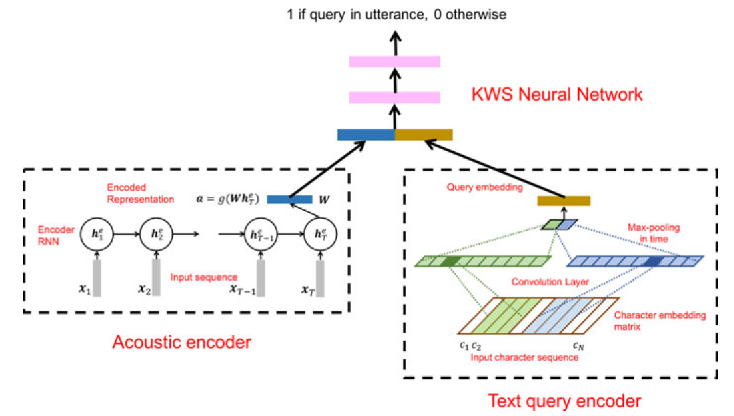
Audhkhasi K, Rosenberg A, Sethy A, et al. End-to-end ASR-free keyword search from speech[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(8): 1351-1359.
Similarity Image Classification For Query-by-Example KWS
如果相似度高,则会连成一个斜线,然后用图像的方法分类出来
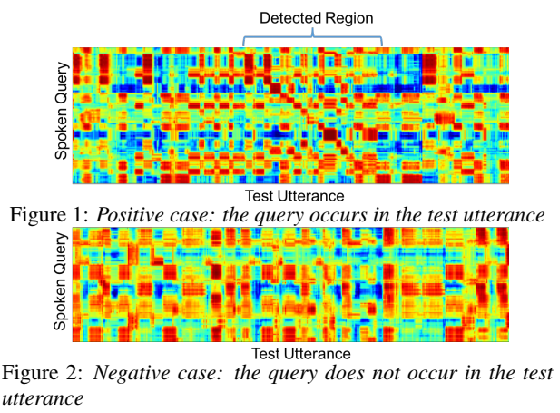
Ram D, Miculicich L, Bourlard H. CNN based query by example spoken term detection[C]//Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH). 2018.
Streaming Seq2Seq Models for KWS
针对关键词检测的流式序列到序列模型。RNN-Transducer是语音识别中的一种端到端方法。它可以分为3个部分:encoder是一个RNN,计算高层声学表示;Prediction Network是一个语言模型,计算预测的Label之间的转移概率;Joint Network则融合前两个模块计算出的表示,做出预测。
CTC存在一个问题,那就是 label之间的关系无法体现出来(比如辅音后面接元音概率大,辅音后面接辅音概率小)
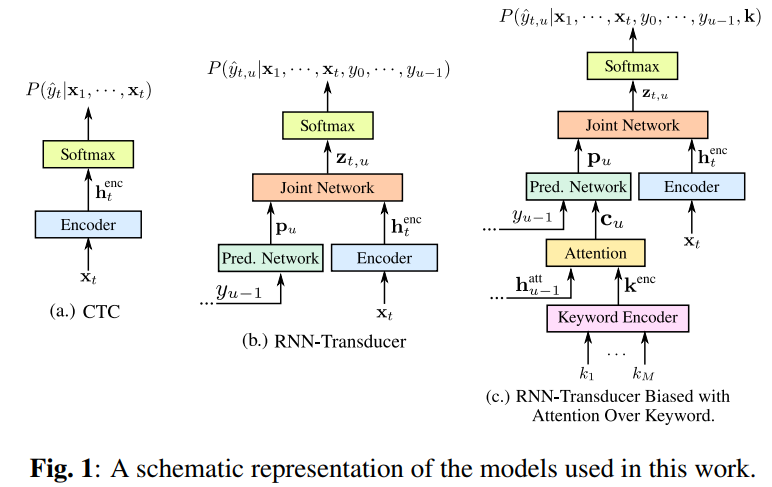
这篇论文在RNN-Transducer的基础上,加入关键词的编码模块与注意力机制,“引导(bias)”RNN-Transducer解码出关键词,提升了关键词检测的准确率。
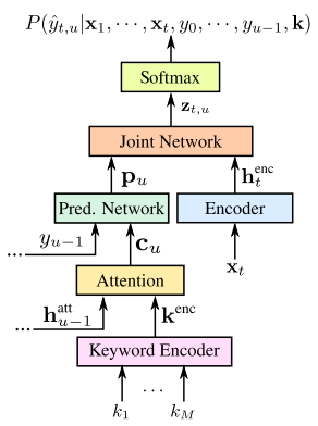
有M个关键词$k^{enc}=[k_1^{enc},…,k_{M}^{enc},k_{M+1}^{enc}]$is one-hot encodings of M+1 phonemes of a keyword.
$$
\large\beta_{j,u}=\langle\phi(k_j^{enc}),\psi(h_{u-1}^{att})\rangle
$$
$$
\large\alpha=\frac{e^{\beta_{j,u}}}{\sum\limits_{j’=1}^{M+1}e^{\beta_{j’,u}}}
$$
$$
\large{c_u=\sum\limits_{j=1}^{M+1}\alpha_{j,u}k_j^{enc}}
$$
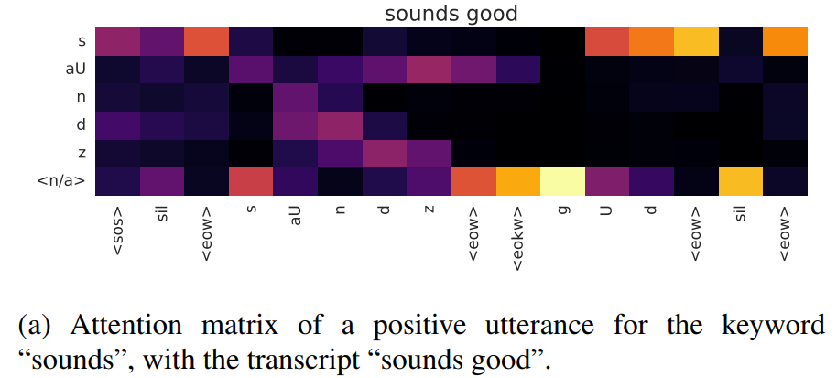
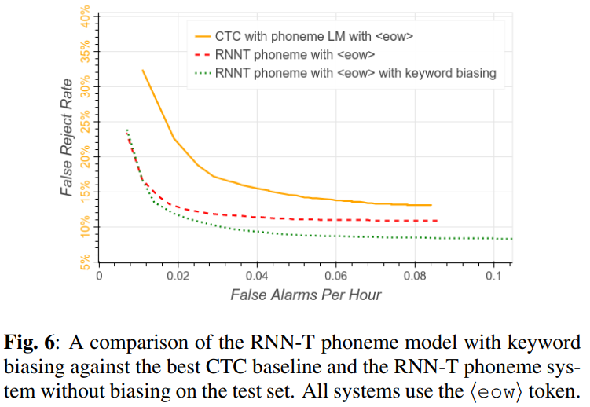
He Y, Prabhavalkar R, Rao K, et al. Streaming small-footprint keyword spotting using sequence-to-sequence models[C]//Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), 2017 IEEE
总结 Take Home Messages
- Keyword spotting focuses on detecting keywords in computation constrained conditions.
- The out-of-vocabulary keywords are problems of spoken term detection.
关键词检测分为两种:KeywordSpotting关注在计算资源有限的情况下,快速准确地从音频流中检测出关键词;Spoken Term Detection中的一大难题是如何检测出集外词。
参考文献
基于隐马尔可夫模型的补白模型
Wilpon JG, Lee C, Rabiner L R, et al. Application of hidden Markov models for recognition of a limited set of words in unconstrained speech[C]. internationalconference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 1989: 254-257.
Sun M,Snyder D, Gao Y, et al. Compressed Time Delay Neural Network for Small-Footprint Keyword Spotting.[C]. conference of the international speechcommunication association, 2017: 3607-3611.
直接用DNN进行分类的补白模型
- Chen G,Parada C, Heigold G, et al. Small-footprint keyword spotting using deep neuralnetworks[C]. international conference on acoustics, speech, and signalprocessing, 2014: 4087-4091.
动态时间弯折
ItakuraF. Minimum prediction residual principle applied to speech recognition[J]. IEEETransactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1975, 23(1): 154-158.
Sakoe H,Chiba S. Dynamic programming algorithm optimization for spoken wordrecognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing,1978, 26(1): 159-165.
MantenaG V, Achanta S, Prahallad K, et al. Query-by-example spoken term detectionusing frequency domain linear prediction and non-segmental dynamic timewarping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2014,22(5): 946-955.
Zhang Y,Glass J R. Unsupervised spoken keyword spotting via segmental DTW on Gaussianposteriorgrams[C]. ieee automatic speech recognition and understandingworkshop, 2009: 398-403.
基于嵌入学习的样例检索
Chen G,Parada C, Sainath T N, et al. Query-by-example keyword spotting using longshort-term memory networks[C]. international conference on acoustics, speech,and signal processing, 2015: 5236-5240.
KamperH, Wang W, Livescu K, et al. Deep convolutional acoustic word embeddings usingword-pair side information[J]. international conference on acoustics, speech,and signal processing, 2016: 4950-4954.
大词汇量连续语音识别的关键词检索:时间因子转换器索引构建
- Can D, Saraclar M. Lattice Indexing for Spoken Term Detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and LanguageProcessing, 2011, 19(8): 2338-2347.
大词汇量连续语音识别的关键词检索:代理词生成
- Chen G, Yilmaz O, Trmal J, et al. Using proxies for OOV keywords in the keyword search task[C]. ieee automatic speechrecognition and understanding workshop, 2013: 416-421.
异质数据相似度计算
- Audhkhasi K, Rosenberg A, Sethy A, et al.End-to-end ASR-free keyword search from speech[J]. IEEE Journal of SelectedTopics in Signal Processing, 2017, 11(8): 1351-1359.
流式端到端识别系统的关键词检测
- He Y, Prabhavalkar R, Rao K, et al. Streaming small-footprint keyword spotting using sequence-to-sequence models[C]//Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), 2017IEEE.